Ignition has two different ways for you to make use of stored procedures within your database: transaction groups, scripting functions. Depending on your specific needs will determine which method you use to call your stored procedures.
You will want to read up on transaction groups and how they generally function if you are not very familiar with them:
General Overview - Introduction, Execution Cycle
Group Anatomy - Action Settings, Trigger and Handshake Settings, Advanced Settings
Group Items - Overview, OPC Item,
Stored Procedure Transaction Groups
Stored procedure groups allow you to target stored procedures in your database as opposed to tables, allowing you to map input and output params directly to your PLC tags. The stored procedure group is set up in much of the same way as all the other types of transaction groups in Ignition, so if you are familiar with how to use standard or historical groups then you should have no real difficulty setting up a stored procedure group. A more detailed description of the stored procedure group can be found here: Stored Procedure Group.
Setting Up a Stored Procedure Group
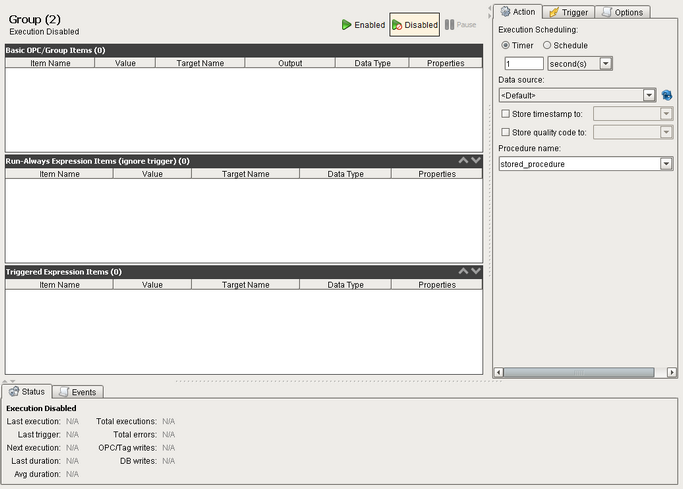
| 1. | In the Ignition designer right click the Transaction Groups icon in the project browser then select "New Transaction Group" -> "New Stored Procedure Group" |
| 2. | From the dropdown box choose the data source in which your stored procedure resides. (If you have not yet made a connection to the database that contains your stored procedure see: How do I connect to a database?) |
| 3. | Once you have selected the data source, the "Procedure name" dropdown should populate with the names of any stored procedures in your database. Select which procedure you would like to use. If your stored procedures aren't listed and you are sure that you have selected the correct data source then simply type the name of the stored procedure in the dropdown box (case sensitive). |
| 4. | Drag in the OPC tags you want your group to use and then assign the to an input param (Target Name) or/and output param (Output) of your stored procedure. The names of your procedure parameters should show up in the dropdown boxes for the Target Name and Output columns, however if they do not show up then just specify the name of the parameter you want to reference omitting any special characters (e.g. @) |
| 5. | Configure any trigger settings you may wish to set up (Trigger and Handshake Settings), and configure and settings in the Options section (Advanced Settings) |
| 6. | Enable the group and save your project. |
It is important to note that not all databases will browse correctly and list your stored procedures and their in/out parameters. Usually just entering the name of the stored procedure or parameter will be sufficient, however there are times when the database will still return an error complaining about not being able to find the correct parameter even after you have entered it exactly as it appears in the stored procedure. In these situations you will usually have to refer to the parameters by their index (usually starting at 0). The index of the parameter corresponds to its position relative to the other procedure parameters when it is declared.
Troubleshooting Group Execution Errors
Remember that the Events tab is a helpful tool for troubleshooting problems with your group execution. Error messages will be displayed under this section and double clicking the different messages will present you with a pop-up that contains more detailed information about the error that occurred. You can usually get a good idea about what exactly is causing your group to throw an error.
Scripting Functions
Ignition has several built in scripting functions that allow you to call stored procedures from event scripts in you project. The process for using these functions is similar to that described in the How do I run a SQL Query from a button? section. A summation of the general steps for using the scripting functions is as follows:
| 1. | Create the call context by calling system.db.createSProcCall |
| 2. | Register any In/Out/Return Params |
| 3. | Execute the call context by calling system.db.execSProcCall |
| 4. | Use the appropriate call context functions to retrieve any output params, a return value or a resultset generated by the stored procedure |
The section for system.db.createSProcCall contains some detailed examples on how to use both the create and exec functions so be sure to read through those thoroughly.