Microsoft SQL Server is a popular robust relational database produced by Microsoft. Ignition can connect to Microsoft SQL Server, however many users find difficulty in getting all of the settings and parameters correct. There are several different ways you can connect to Microsoft SQL Server (all using TCP/IP communication):
| • | Specifying a Port using Windows Authentication |
| • | Specifying an Instance Name using Windows Authentication |
| • | Specifying a Port using SQL Authentication |
| • | Specifying an Instance Name using SQL Authentication |
The most common method, the one out of the box, is to connect using an Instance Name and Windows Authentication.
SQL Server Instances
Microsoft SQL Server supports multiple instances of the database running concurrently on the same computer. Each instance has its own name and set of system and user databases that are not shared between instances. Applications, such as Ignition, can connect to each instance on a computer in much the same way they connect to databases running on different computers. Each instance gets assigned a dynamic TCP/IP port on startup that it will listen on for any incoming requests. Since the port is dynamic and the application will not know what the new port is, it must connect using the instance name.
If the communication is over TCP/IP and the application knows the instance name, how will the application find which port to communicate over?
The answer is the Microsoft SQL Server Browser Service. The Microsoft SQL Server Browser program runs as a Windows service and listens for all incoming requests for resources and provides information, such as the TCP/IP port, about each instance installed on the computer. Microsoft SQL Server Browser also contributes to the following actions:
| • | Browsing a list of available servers |
| • | Connecting to the correct server instance |
If the Microsoft SQL Server Browser service is not running, you are still able to connect to SQL Server if you provide the correct port number. For instance, you can connect to the default instance of SQL Server with TCP/IP if it is running on port 1433.
Check 1: Make Sure the Database has TCP/IP Enabled
Ignition connects using TCP/IP, so the first step is to make sure your database has TCP/IP enabled. To check:
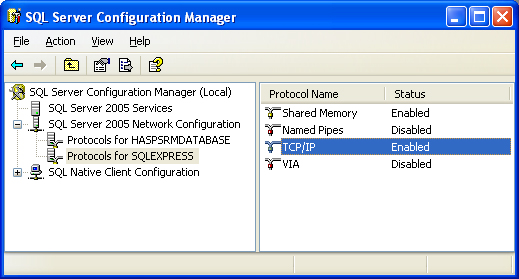
| 1. | Open up the SQL Server Configuration Manager from Start > All Programs > Microsoft SQL Server Version # > Configuration Tools > SQL Server Configuration Manager. |
| 2. | Once it is open, you will see all of the instances setup on that machine by expanding "SQL Server Version # Network Configuration". |
| 3. | Find the database (or instance) you plan on using and click on it. |
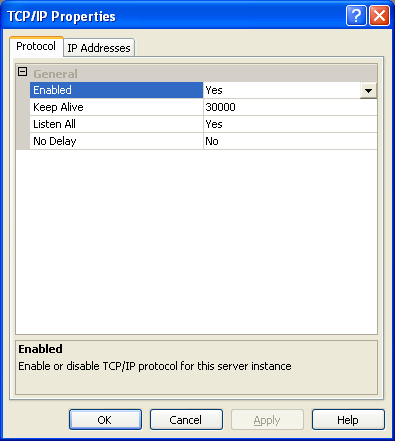
| 4. | To the right you will see all of the protocols the database supports. One of the protocols is TCP/IP. Make sure the status next to TCP/IP is set to Enabled. If not, double click on "TCP/IP" and choose Yes from the drop-down next to Enabled and press OK. |
Check 2: Make Sure Microsoft SQL Server Browser is Running
If you ARE connecting to your database using a NAMED INSTANCE you must make sure that the Microsoft SQL Server Browser is running. As mentioned earlier, the Microsoft SQL Server Browser translates the instance name to a TCP/IP port in order for your application (Ignition) to connect to it. To check:
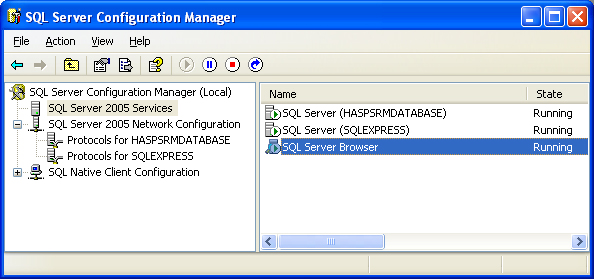
| 1. | Open up the SQL Server Configuration Manager from Start > All Programs > Microsoft SQL Server Version # > Configuration Tools > SQL Server Configuration Manager. |
| 2. | Once it is open, select the "SQL Server Version # Services" section. |
| 3. | To the right you will see all of the services installed. One of the services is the "SQL Server Browser". Make sure this service is in fact running. If the service is not running, right click and select Start. |
Note: The service could be disabled so you may have to double click on it to enable the service before starting it up.
Scenario 1: Connecting Using Instance Name and SQL Authentication
Since we are using SQL authentication, Microsoft SQL Server must allow this type of authentication. By default, Microsoft SQL Server only allows Windows authentication since it is more secure. To enable:
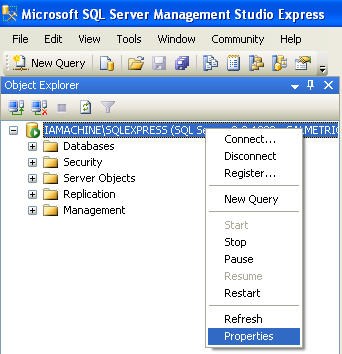
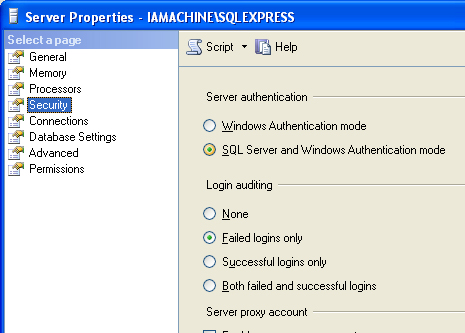
| 1. | Open the SQL Server Management Studio from Start > All Programs > Microsoft SQL Server Version # > SQL Server Management Studio. |
| 2. | Once open and connected to your database, right click on the top level database in the Object Explorer and select Properties. |
| 3. | Select Security on the left hand side. |
| 4. | Verify that "SQL Server and Windows Authentication" mode is selected. If not, select it and press OK. |
| 5. | You will have to restart the "SQL Server Windows" service for this setting to take effect. Open the "SQL Server Configuration Manager" (from previous steps) and restart the "SQL Server (Instance Name)" item from the "SQL Server Services" section. |
Now that Microsoft SQL Server accepts SQL authentication we can move to configuring Ignition. Follow these steps:
| 1. | Open and login into the Ignition Gateway configuration page from your web-browser. (http://hostname:8088/main/web/config) |
| 2. | Select Databases > Connections from the menu. |
| 3. | Click "Create new Database Connection" |
| 4. | Select the "Microsoft SQL Server JDBC Driver" and press next. |
| 5. | Give the connection a name like "SQL Server SQL Auth" |
| 6. | Set the "Connect URL" to: |
jdbc:sqlserver://Hostname\InstanceName
Replace the "Hostname" with your databases IP address or hostname and replace the "InstanceName" with your databases instance name. Here are a couple of examples:
jdbc:sqlserver://localhost\SQLEXPRESS
jdbc:sqlserver://10.10.1.5\MSSQLSERVER
| 7. | Set the username and password to a valid SQL authentication user. For example, "sa" is an administrator account you can use. To add your own user account open the "SQL Server Management Studio", expand the Security > Logins folder. There you can see all of the current logins. Right click on the Logins folder and click "New Login...". Choose the SQL Server authentication mode and type in a username and password. Note: You will also have to add permissions to your database by mapping "db_datareader" and "db_datawriter" to the new user in the "User Mapping" section. |
| 8. | Lastly, set the "Extra Connection Properties" to your database. For example: |
databaseName=test
Replace "test" with your database name.
| 9. | Press "Create New Database Connection" and the status should be Valid after a couple of seconds. |
If the connection is "Faulted" click on the "Database Connection Status" link to find out why. Typically the username/password is incorrect or the user doesn't have the right permissions.
Scenario 2: Connecting Using Instance Name and Windows Authentication
In Windows authentication mode, the username and password used to connect comes from the Ignition Windows Service logon. By default, the Ignition Windows Service is set to local system account which usually doesn't have privileges to connect. To connect using Windows authentication:
| 1. | First we have to download the necessary microsoft .dll files. We have made these available to here: |
http://files.inductiveautomation.com/sqlserver_winauth_dlls/auth.zip
| 2. | Extract the files to your desktop. Locate the sqljdbc_auth.dll from the correct architecture folder (x86 for 32-bit and x64 for 64-bit) |
| 3. | Copy the sqljdbc_auth.dll file to the following location: |
C:\Program Files\Inductive Automation\Ignition\lib\
| 4. | Now let's setup Ignition to logon using the right Windows account. Open the "Services Control Panel" from Start > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services. |
| 5. | Right click on the "Ignition" service and choose "Properties". |
| 6. | Select the "Log On" tab. |
| 7. | Choose "This Account" and enter in your Windows username and password. Press OK to save. |
| 8. | Restart the Ignition service by either clicking the restart button in the toolbar or stopping and starting from the right click menu. |
Now we can move to configuring the database connection in Ignition. Follow these steps:
| 1. | Open and login into the Ignition Gateway configuration page from your web-browser. (http://hostname:8088/main/web/config) |
| 2. | Select Databases > Connections from the menu. |
| 3. | Click "Create new Database Connection" |
| 4. | Select the "Microsoft SQL Server JDBC Driver" and press next. |
| 5. | Give the connection a name like "SQL Server Windows Auth" |
| 6. | Set the "Connect URL" to: |
jdbc:sqlserver://Hostname\InstanceName
Replace the "Hostname" with your databases IP address or hostname and replace the "InstanceName" with your databases instance name. Here are a couple of examples:
jdbc:sqlserver://localhost\SQLEXPRESS
jdbc:sqlserver://10.10.1.5\MSSQLSERVER
| 7. | Leave the username and password blank. |
| 8. | Lastly, set the "Extra Connection Properties" to your database and set it to use "Integrated Security". For example: |
databaseName=test; integratedSecurity=true;
Replace "test" with your database name.
| 9. | Press "Create New Database Connection" and the status should be Valid after a couple of seconds. |
Again, if the connection is "Faulted" click on the "Database Connection Status" link to find out why.
Scenario 3: Connecting Using Port and SQL Authentication
Connecting using a port and SQL authentication is just like scenario 1 above except we specify a port instead of the instance name. Set the "Connect URL" in step 6 to:
jdbc:sqlserver://Hostname:Port
Replace the "Hostname" with your databases IP address or hostname and replace the "Port" with your databases TCP/IP port. Here are a couple of examples:
jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433
jdbc:sqlserver://10.10.1.5:1433
Scenario 4: Connecting Using Port and Windows Authentication
Connecting using a port and Windows authentication is just like scenario 2 above except we specify a port instead of the instance name. Set the "Connect URL" in step 6 to:
jdbc:sqlserver://Hostname:Port
Replace the "Hostname" with your databases IP address or hostname and replace the "Port" with your databases TCP/IP port. Here are a couple of examples:
jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433
jdbc:sqlserver://10.10.1.5:1433
Common Problems
TCP/IP Communication Not Enabled
SQL Server requires that you explicitly turn on TCP connectivity. To do this, use the SQL Server Configuration Manager, located in the Start menu under "Microsoft SQL Server>Configuration Tools". Under "SQL Server Network Configuration", select your instance, and then enable TCP/IP in the panel to the right. You will need to restart the server for the change to take affect.
Window Firewall
When connecting remotely, make sure that Windows Firewall is disabled, or set up to allow the necessary ports. Normally ports 1434 and 1433 must be open for TCP traffic, but other ports may be required based on configuration.
SQL Server Browser Process Not Running
To connect to a named instance, the "SQL Server Browser" service must be running. It is occasionally disabled by default, so you should verify that the service is not only running, but set to start automatically on bootup. The service can be found in the Windows Service Manager (Control Panel>Administrative Tools>Services).
Mixed Mode Authentication Not Enabled
Unless selected during setup, "mixed mode" or "SQL authentication" is not enabled by default. This mode of authentication is the "username/password" scheme that most users are used to. When not enabled, SQL Server only allows connections using Windows Authentication. Due to the ease of using SQL Authentication over Windows Authentication, we recommend enabling this option and defining a user account for Ignition.
To enable this, open the SQL Server Management Studio and connect to the server. Right click on the instance and select "Properties". Under "Security", select "SQL Sever and Windows Authentication mode".